Volume 13, Issue 2 (4-2025)
J. Pediatr. Rev 2025, 13(2): 95-106 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Rostami-Maskopaee F, Asadi-Aliabadi M, Moosazadeh M, Sadegh Rezai M. Achievements of the PERSIAN Birth Cohorts: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Rev 2025; 13 (2) :95-106
URL: http://jpr.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-701-en.html
URL: http://jpr.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-701-en.html
Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee1 

 , Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi2
, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi2 

 , Mahmood Moosazadeh3
, Mahmood Moosazadeh3 

 , Mohammad Sadegh Rezai *4
, Mohammad Sadegh Rezai *4 




 , Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi2
, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi2 

 , Mahmood Moosazadeh3
, Mahmood Moosazadeh3 

 , Mohammad Sadegh Rezai *4
, Mohammad Sadegh Rezai *4 


1- Pediatric Infectious Diseases Research Center, Communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran. & Student Research Committee, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
2- Health Sciences Research Center, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
3- Gastrointestinal Cancer Research Center, Non-communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
4- Pediatric Infectious Diseases Research Center, Communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran. ,drmsrezaii@yahoo.com
2- Health Sciences Research Center, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
3- Gastrointestinal Cancer Research Center, Non-communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran.
4- Pediatric Infectious Diseases Research Center, Communicable Diseases Institute, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran. ,
Full-Text [PDF 678 kb]
(697 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (1786 Views)
Full-Text: (449 Views)
Introduction
Abirth cohort study is a subset of cohort studies in which a group of individuals sharing some characteristic is followed up over time [1]. The objective of the prospective birth cohort study collecting extensive data starting from the prenatal and early postnatal life periods is to investigate social, environmental, psychological, and genetic factors on the mother, and child’s health [2-5].
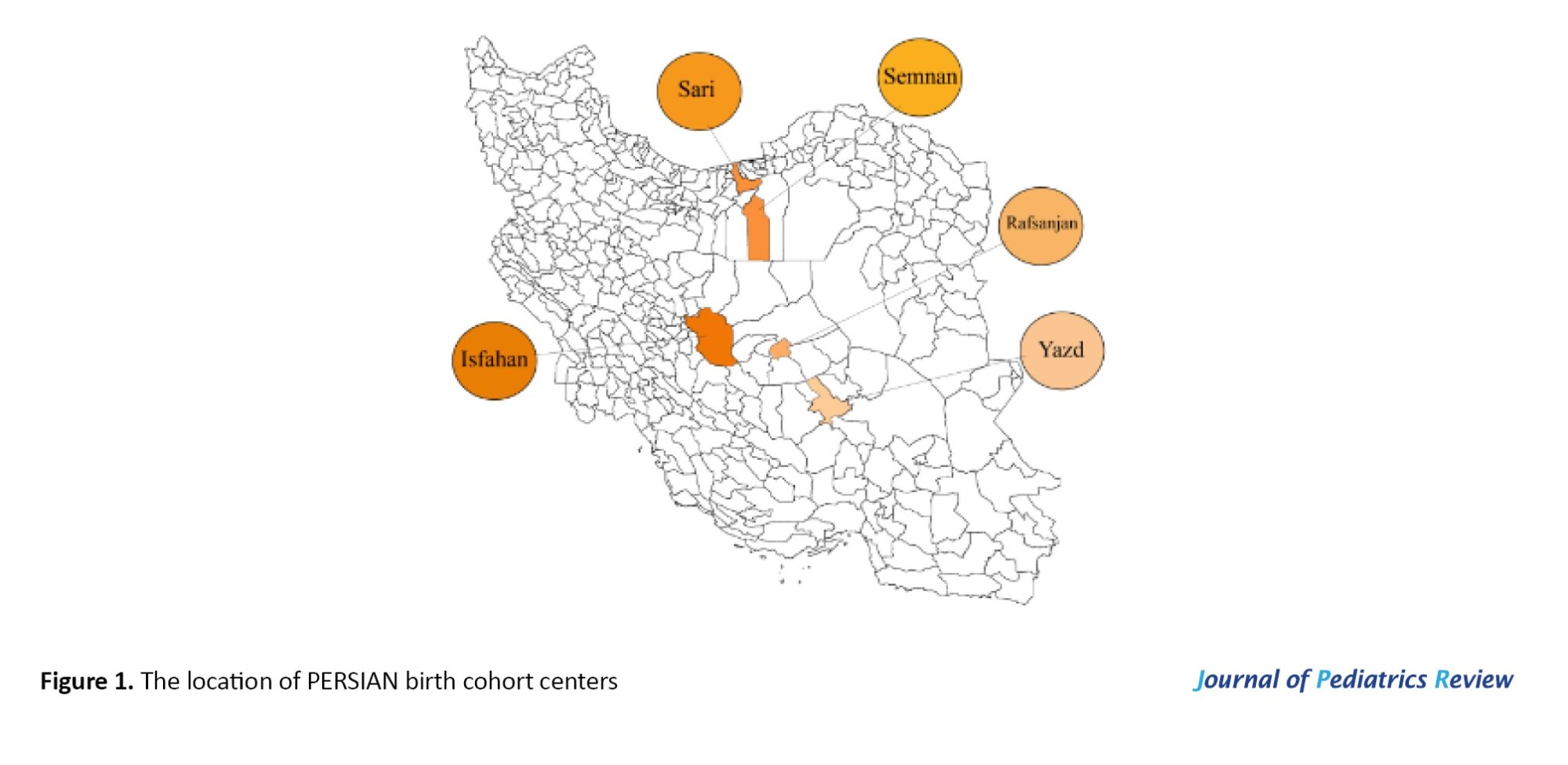
National cohort studies have been established since 2013 under the title of prospective epidemiological research studies in Iran (PERSIAN). It is one of the pioneers of developmental origins of health and diseases research in the Middle East and North Africa region. The PERSIAN birth cohort study is a branch of the PERSIAN cohort. The PERSIAN birth cohort study, with a population of about 15000 pregnant women, was started in five medical universities (Isfahan, Yazd, Semnan, Kerman, and Mazandaran) during 2016-2017 (Figure 1). The large sample size and diverse population of the PERSIAN birth cohort provide a valuable resource for advancing developmental origins of health and disease research. The study protocol was approved by the Iranian Ministry of Health and Medical Education institutional Ethics Committee [6]. The participants met the following inclusion criteria: Being pregnant, of Iranian nationality, residing in the designated geographical area for at least one year, providing informed consent to participate, and agreeing to comply with follow-up requirements. The participants were excluded from the PERSIAN birth cohorts if any of the following occurred adverse pregnancy outcomes, maternal or child death, migration out of the study area, or unwillingness to continue participating. At the first visit, prenatal data were collected by using face-to-face interviews. The children were assessed at birth, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 months; thereafter, they will be followed annually.
Overall, birth cohort studies play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of health development over a lifetime by enabling researchers to explore the complex interplay of early-life factors and their long-term effects on health outcomes [2, 3, 7]. For this purpose, many birth cohorts have been established globally. Some birth cohorts were established with an interest in a single type of outcome, while more birth cohorts tend to study broad areas to encompass any factors influencing child health and opportunities for prevention [2, 7]. Understanding the research areas addressed by the birth cohort center is crucial. This knowledge allows for the design of new cohorts that contribute to scientific knowledge while preventing the waste of valuable resources [2, 7, 8].
To the best of our knowledge, there is not enough information about the number of published articles and the research area among the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. At a time when PERSIAN birth cohort studies are ongoing, it is necessary to review published scientific articles and identify areas for future research collaboration within Iran and internationally.
Methods
This study was conducted as a systematic review, following the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses guidelines.
Search strategy
We systematically searched the international database (PubMed and Web of Science [WOS]) and Iranian database (scientific information database (SID), IranMedex, and Magiran) to identify eligible articles. The search strategies in Persian and English keywords were used between January 2016 and November 2024. Search strategies based on Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were as follows: “Iran” and “birth cohort.” Additionally, we utilized “PERSIAN” terms for manual searches. The research question of this study was to compare the achievements of PERSIAN birth cohorts across five centers. The population and outcome of the study were five birth cohort centers, and the published studies from the birth cohort database, respectively.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria consisted of: 1) Studies published in both Persian and English languages since the beginning of 2016, and 2) Studies related to the PERSIAN birth cohort. Meanwhile, the exclusion criteria were: 1) Conference papers, dissertations, proposals, and letters to the editor, 2) Unavailability of the full text of the studies, and 3) Other birth cohorts in Iran.
Data extraction
The search for these studies was conducted by two authors (Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi) independently. Disagreements were settled through the involvement of third reviewers (Mohammad Sadegh Rezai, Mahmood Moosazadeh). The references of eligible studies were searched manually to identify further research. After importing all included studies into EndNote Software, version 20, duplicate studies were identified and removed. Subsequently, abstracts of eligible studies were reviewed, and then the full texts were evaluated. The information from the included studies was extracted as follows: Names of authors, year of publication, location of the birth cohort center, type of study, language, title of study, and area of research.
To identify the research areas of the studies conducted under the PERSIAN birth cohort protocol, the research domains were divided into five subcategories: 1) Registration and general information, 2) Mental health and lifestyle, 3) Environmental and occupational exposures, 4) Nutrition and diet, and 5) Medical information [6]. The lifestyle domain included issues such as physical activity, sleep patterns, risky behaviors like smoking, alcohol consumption, and substance abuse or addiction. Meanwhile, environmental exposures were air pollution (outdoor and indoor), noise pollution, radiations (ionizing, ultraviolet, and non-ionizing), water pollutants, allergens and biological organisms, metals, pesticides, tobacco smoke (active and passive), and other chemical compounds [6, 9].
Results
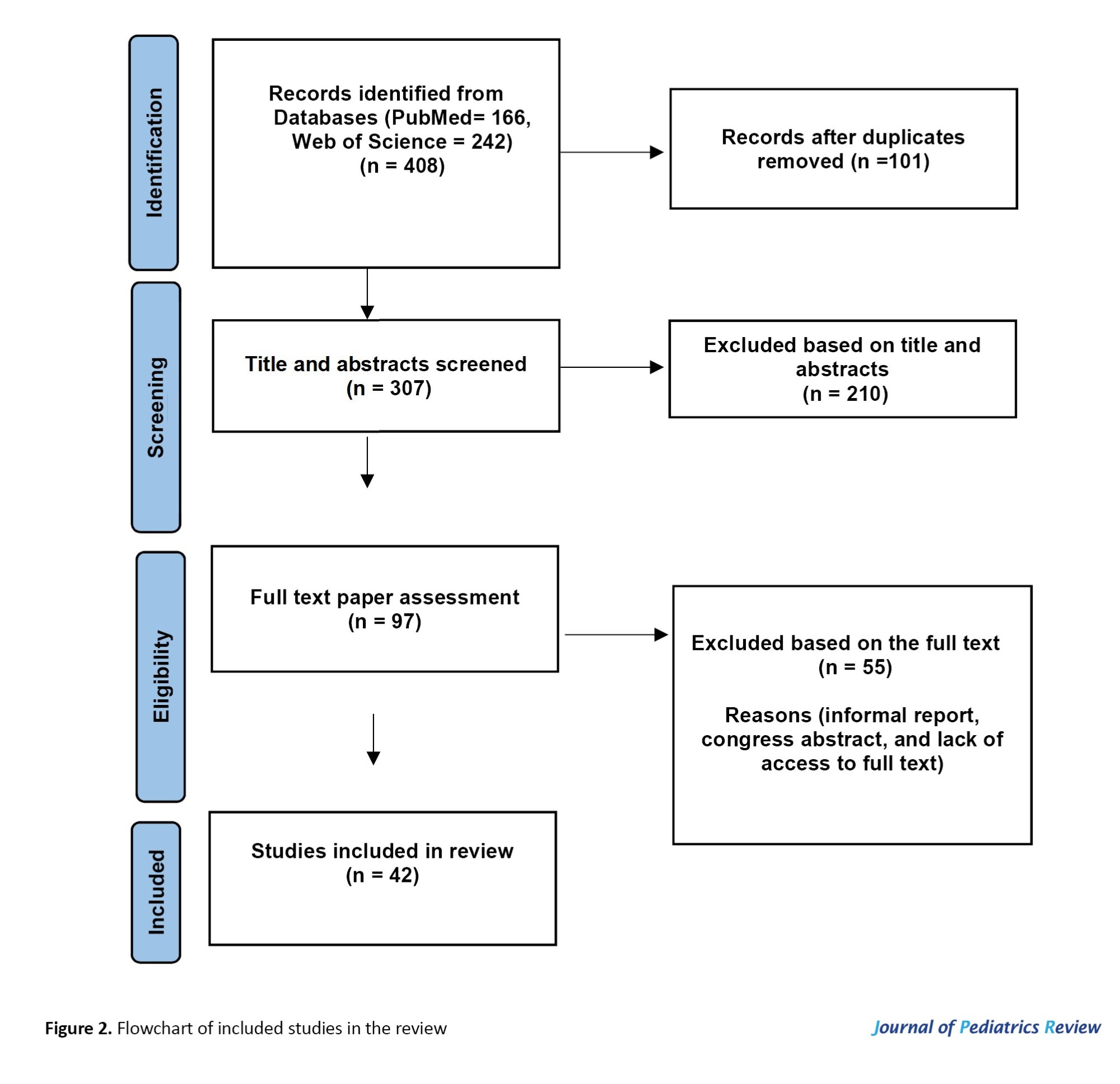
A total of 408 articles (166 PubMed and 242 WOS) were published from the PERSIAN birth cohort in international and national databases. Among the included articles, 101 duplicates were identified and excluded. Conference abstracts and informal reports were not included in this review. Finally, 42 studies were selected from five PERSIAN birth cohort centers (Figure 2).
All studies are listed in Table 1. Of the 42 articles, 39(92.85%) were published in English, while the others were in Persian. The design of most studies has been observational (cross-sectional and cohort studies).
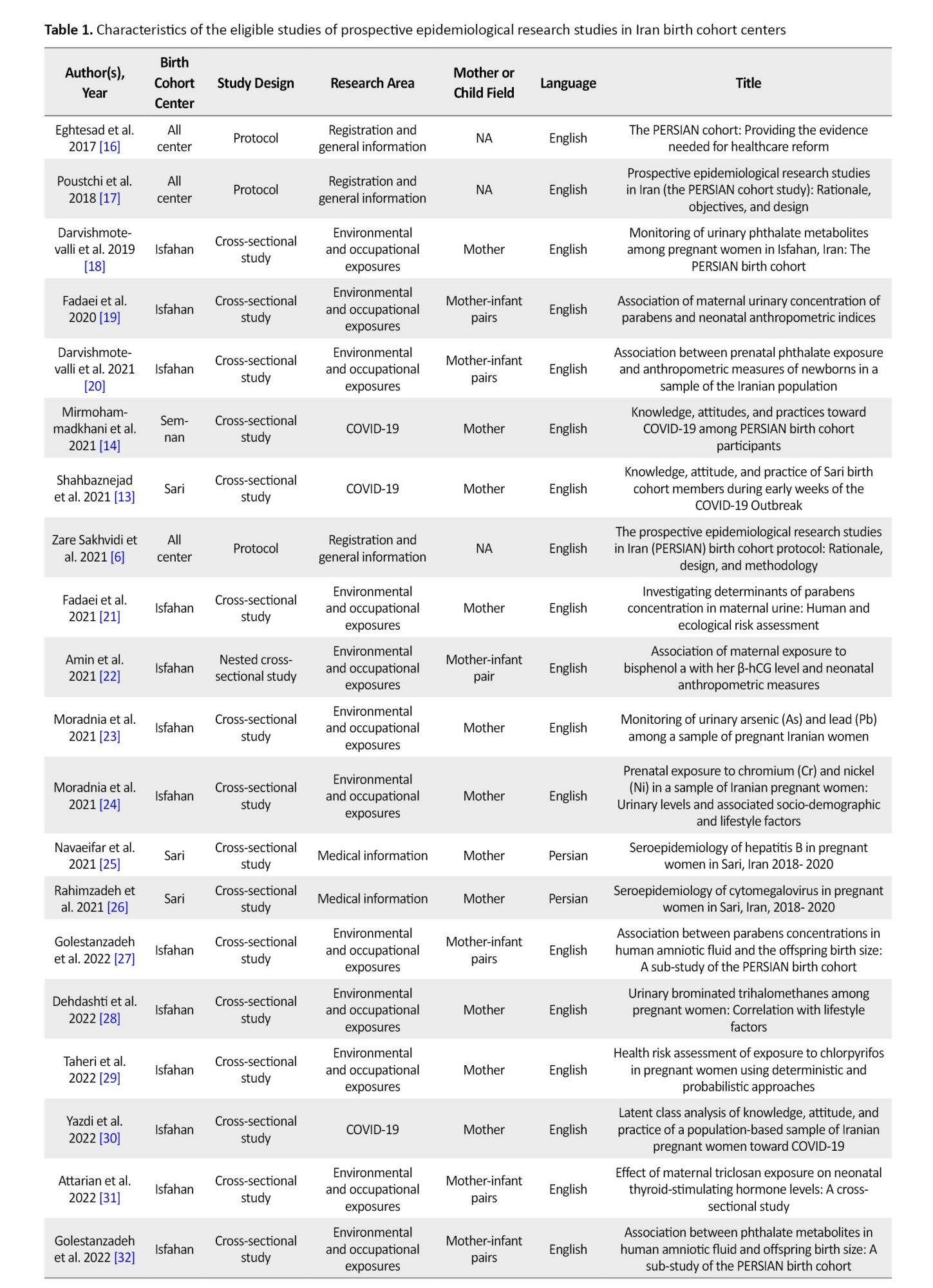
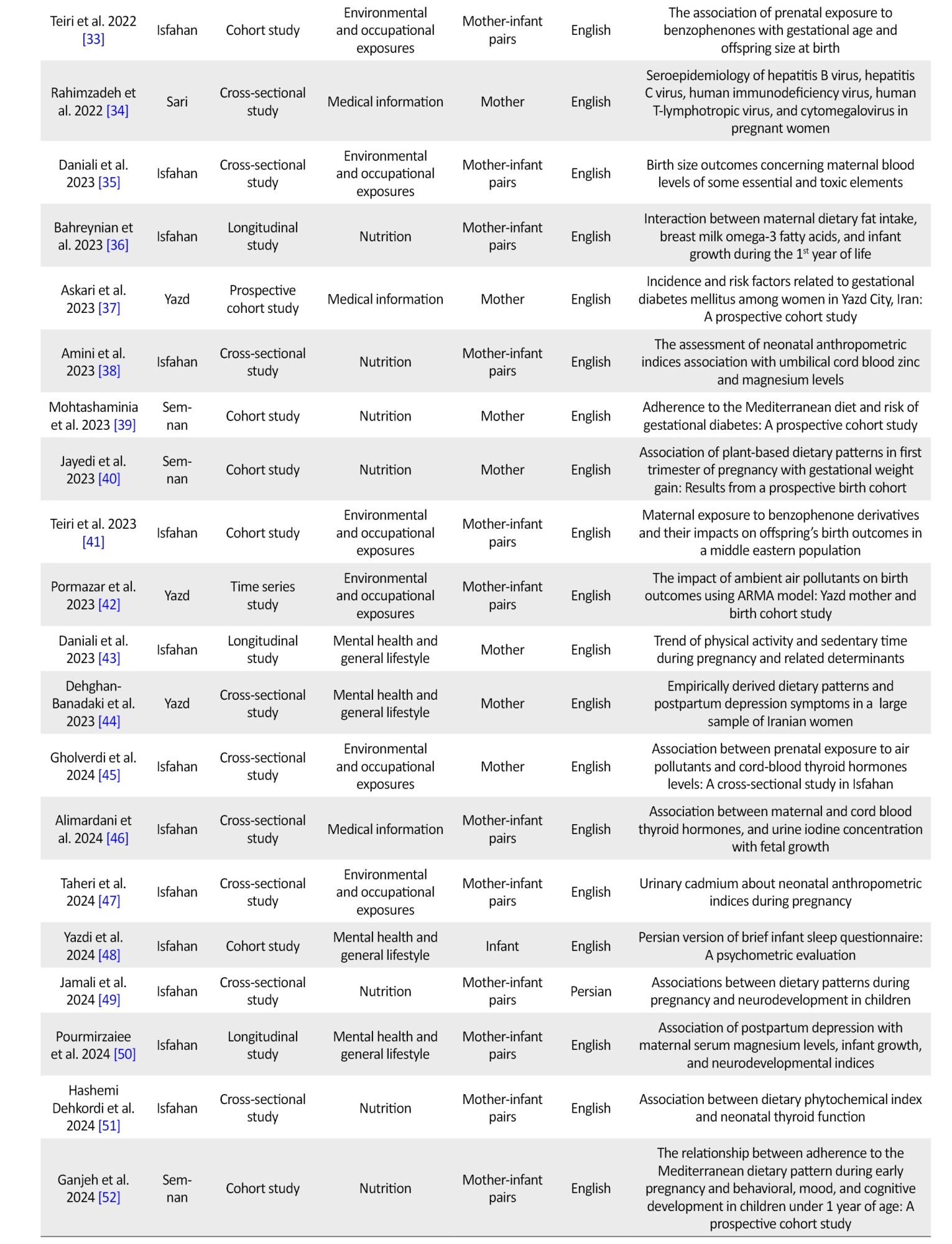
The publication dates of the articles ranged from 2017 to 2024. The number of scientific articles showed an increasing trend during this period. The total number of articles published in 2021, 2023, and 2024 is 10 articles for each of the years. Among the five birth cohort centers, the Isfahan center had the highest number of published scientific articles (27), followed by Seaman (5) and Sari (4), respectively. The number of articles published from Isfahan increased from 1 in 2017 to 8 in 2024.
The titles of the studies included in this systematic review were varied. Of the studies, 47.62% (20 out of 42) were only related to the mother, 42.86% (18 out of 42) addressed both the mother and the child, and 2.38% (1 out of 42) focused solely on the child. Additionally, three of the 42 studies (7.14%) pertained to the protocol of birth cohort.
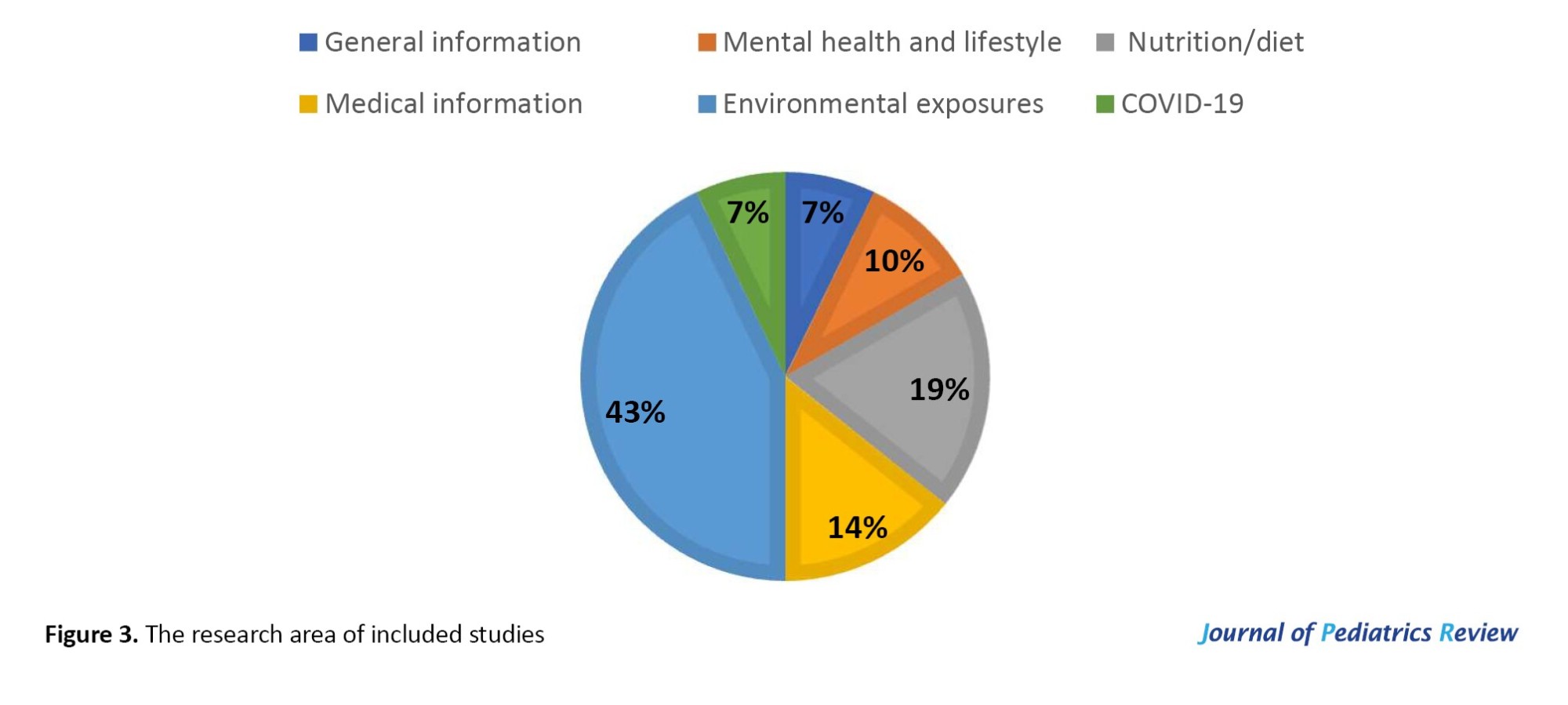
The number of published scientific articles was in the following areas of research: Registration and general information (3), mental health and general lifestyle (4), nutrition/diet (8), medical information (6), environmental and occupational exposures (18). Additionally, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, 7.14% (3 out of 42) of published studies were focused on COVID-19 research (Figure 3).
Discussion
We conducted this systematic review to survey the achievements of the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. Accordingly, the numbers of articles were increased during 2017-2024. The majority of the birth cohort studies focused on the field of maternal health. Also, the most common research area among the five birth cohorts was environmental and occupational exposures.
The environmental factors, such as air pollution, allergens, pesticides, radiation, and chemical exposures during pregnancy, can significantly influence pregnancy outcomes and the long-term health of the child [6]. In Pandolfni’s study, consistent with our findings, environment research was a priority research area for cohorts in Europe [2]. Achievements of other birth cohort centers worldwide have provided information on immune disorders (such as allergic diseases and asthma), environmental exposure, neurocognitive development/neurobehavioral disorders, and nutrition [8-10]. In a review conducted by Vrijheid et al., growth and obesity, allergies, asthma, and respiratory infections were assessed in nearly all European birth cohorts [9].
Birth cohort studies across the globe have distinct original goals, yet they have also expanded into new research domains influenced by varying geographic contexts. In Brazil, for instance, violence represents a critical health and social issue, ranking as the leading cause of mortality among children and adolescents [4]. Hence, a new focus of the cohort is to understand the effects of violence on child development and health. A new area for research is the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and children’s health and the birth cohort achievements [7, 11]. According to the experiences of birth cohort centers in the world, face-to-face interviews were suspended during the COVID-19 pandemic [7, 12]. In Pearson’s study [12], COVID-19 changed the way the study team interacted with the cohort and impacted the cohort’s health outcomes. The PERSIAN birth cohort teams from five universities made efforts to carry out research related to COVID-19, aligning with the policies of the Corona National Anti-Virus Headquarters, and the Minister of Health and Medical Education [13, 14]. During the COVID-19 pandemic, facilities such as distributing preventive measures like alcohol, gloves, and masks, as well as conducting polymerase chain reaction tests, were provided.
The designs of the majority of published studies are observational; however, they serve as a suitable platform for clinical research. Involving pregnant women in research studies is crucial for gathering essential information about the safety and effectiveness of therapeutics or interventions aimed at improving maternal health and pregnancy outcomes [15]. Since pregnant women are typically excluded from randomized controlled trials for ethical reasons, it is difficult to evaluate the safety of drugs used during pregnancy. In this regard, designs of observational population-based cohort studies offer an alternative to randomized controlled trials [3]. This approach can yield valuable insights without the costs, risks, and ethical concerns associated with clinical trials.
Among the five centers, the Isfahan birth cohort center produced the most published scientific articles, followed by Semnan and Sari, respectively. The findings also revealed that the majority of scientific articles have originated from a single center. Multi-center studies can pool resources and expertise, enhancing the overall quality of research. The birth cohort studies can be a suitable platform for sharing data to achieve their common goals.
To enhance future birth cohort studies in Iran, several practical suggestions can be made based on the current structure and objectives of the PERSIAN Birth Cohort. We suggest that the PERSIAN birth cohort engage in collaborative efforts to enhance the study’s validity. Future studies should focus on incorporating a wider diversity of ethnicities and geographical regions. This will facilitate the identification of the distinct cultural, genetic, and environmental factors that impact health outcomes. Also, integrating socioeconomic status into the study design can offer valuable insights into health disparities. Evidence from studies highlights the significant influence of socioeconomic factors on health outcomes. By adopting these practical recommendations, future birth cohort studies can achieve more meaningful results that significantly enhance public health knowledge and lead to interventions specifically designed to meet the needs of the Iranian population.
Conclusion
The results of this review showed that the environmental and occupational exposures in the maternal field were the most common research area, deriving from five PERSIAN birth cohorts. The findings also indicated that most studies were conducted independently. Consequently, it is recommended that the five PERSIAN birth cohort centers collaborate in future research to identify the cultural, genetic, and environmental factors that influence health outcomes.
Study strengths and limitations
Based on the available knowledge, this study is the only document that focuses on the achievements related to the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. The main limitation of our research was the lack of access to the full text of some studies, which hindered our ability to identify the study design and research area. In response, we contacted the authors of those studies and requested that they provide us with the full text of their articles. Despite our efforts to address this issue, we have no access to the full text of some studies. Additionally, identifying the research area in some studies was difficult.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran (Code: IR.MAZUMS.REC.1401.464).
Funding
This study was funded by the Deputy of Research and Technology of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran (Code: 15032).
Authors contributions
Conceptualization, supervision: Mohammad Sadegh Rezai; Data curation, writing the original draft: Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, and Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi; Review, and editing: Mohammad Sadegh Rezai, Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi, and Mahmood Moosazadeh; Final approval: All authors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors are deeply thankful to the members of the PERSIAN birth cohort research team from five universities of medical sciences.
References
Abirth cohort study is a subset of cohort studies in which a group of individuals sharing some characteristic is followed up over time [1]. The objective of the prospective birth cohort study collecting extensive data starting from the prenatal and early postnatal life periods is to investigate social, environmental, psychological, and genetic factors on the mother, and child’s health [2-5].
National cohort studies have been established since 2013 under the title of prospective epidemiological research studies in Iran (PERSIAN). It is one of the pioneers of developmental origins of health and diseases research in the Middle East and North Africa region. The PERSIAN birth cohort study is a branch of the PERSIAN cohort. The PERSIAN birth cohort study, with a population of about 15000 pregnant women, was started in five medical universities (Isfahan, Yazd, Semnan, Kerman, and Mazandaran) during 2016-2017 (Figure 1). The large sample size and diverse population of the PERSIAN birth cohort provide a valuable resource for advancing developmental origins of health and disease research. The study protocol was approved by the Iranian Ministry of Health and Medical Education institutional Ethics Committee [6]. The participants met the following inclusion criteria: Being pregnant, of Iranian nationality, residing in the designated geographical area for at least one year, providing informed consent to participate, and agreeing to comply with follow-up requirements. The participants were excluded from the PERSIAN birth cohorts if any of the following occurred adverse pregnancy outcomes, maternal or child death, migration out of the study area, or unwillingness to continue participating. At the first visit, prenatal data were collected by using face-to-face interviews. The children were assessed at birth, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 months; thereafter, they will be followed annually.

Overall, birth cohort studies play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of health development over a lifetime by enabling researchers to explore the complex interplay of early-life factors and their long-term effects on health outcomes [2, 3, 7]. For this purpose, many birth cohorts have been established globally. Some birth cohorts were established with an interest in a single type of outcome, while more birth cohorts tend to study broad areas to encompass any factors influencing child health and opportunities for prevention [2, 7]. Understanding the research areas addressed by the birth cohort center is crucial. This knowledge allows for the design of new cohorts that contribute to scientific knowledge while preventing the waste of valuable resources [2, 7, 8].
To the best of our knowledge, there is not enough information about the number of published articles and the research area among the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. At a time when PERSIAN birth cohort studies are ongoing, it is necessary to review published scientific articles and identify areas for future research collaboration within Iran and internationally.
Methods
This study was conducted as a systematic review, following the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses guidelines.
Search strategy
We systematically searched the international database (PubMed and Web of Science [WOS]) and Iranian database (scientific information database (SID), IranMedex, and Magiran) to identify eligible articles. The search strategies in Persian and English keywords were used between January 2016 and November 2024. Search strategies based on Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were as follows: “Iran” and “birth cohort.” Additionally, we utilized “PERSIAN” terms for manual searches. The research question of this study was to compare the achievements of PERSIAN birth cohorts across five centers. The population and outcome of the study were five birth cohort centers, and the published studies from the birth cohort database, respectively.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria consisted of: 1) Studies published in both Persian and English languages since the beginning of 2016, and 2) Studies related to the PERSIAN birth cohort. Meanwhile, the exclusion criteria were: 1) Conference papers, dissertations, proposals, and letters to the editor, 2) Unavailability of the full text of the studies, and 3) Other birth cohorts in Iran.
Data extraction
The search for these studies was conducted by two authors (Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi) independently. Disagreements were settled through the involvement of third reviewers (Mohammad Sadegh Rezai, Mahmood Moosazadeh). The references of eligible studies were searched manually to identify further research. After importing all included studies into EndNote Software, version 20, duplicate studies were identified and removed. Subsequently, abstracts of eligible studies were reviewed, and then the full texts were evaluated. The information from the included studies was extracted as follows: Names of authors, year of publication, location of the birth cohort center, type of study, language, title of study, and area of research.
To identify the research areas of the studies conducted under the PERSIAN birth cohort protocol, the research domains were divided into five subcategories: 1) Registration and general information, 2) Mental health and lifestyle, 3) Environmental and occupational exposures, 4) Nutrition and diet, and 5) Medical information [6]. The lifestyle domain included issues such as physical activity, sleep patterns, risky behaviors like smoking, alcohol consumption, and substance abuse or addiction. Meanwhile, environmental exposures were air pollution (outdoor and indoor), noise pollution, radiations (ionizing, ultraviolet, and non-ionizing), water pollutants, allergens and biological organisms, metals, pesticides, tobacco smoke (active and passive), and other chemical compounds [6, 9].
Results
A total of 408 articles (166 PubMed and 242 WOS) were published from the PERSIAN birth cohort in international and national databases. Among the included articles, 101 duplicates were identified and excluded. Conference abstracts and informal reports were not included in this review. Finally, 42 studies were selected from five PERSIAN birth cohort centers (Figure 2).

All studies are listed in Table 1. Of the 42 articles, 39(92.85%) were published in English, while the others were in Persian. The design of most studies has been observational (cross-sectional and cohort studies).



The publication dates of the articles ranged from 2017 to 2024. The number of scientific articles showed an increasing trend during this period. The total number of articles published in 2021, 2023, and 2024 is 10 articles for each of the years. Among the five birth cohort centers, the Isfahan center had the highest number of published scientific articles (27), followed by Seaman (5) and Sari (4), respectively. The number of articles published from Isfahan increased from 1 in 2017 to 8 in 2024.
The titles of the studies included in this systematic review were varied. Of the studies, 47.62% (20 out of 42) were only related to the mother, 42.86% (18 out of 42) addressed both the mother and the child, and 2.38% (1 out of 42) focused solely on the child. Additionally, three of the 42 studies (7.14%) pertained to the protocol of birth cohort.
The number of published scientific articles was in the following areas of research: Registration and general information (3), mental health and general lifestyle (4), nutrition/diet (8), medical information (6), environmental and occupational exposures (18). Additionally, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, 7.14% (3 out of 42) of published studies were focused on COVID-19 research (Figure 3).

Discussion
We conducted this systematic review to survey the achievements of the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. Accordingly, the numbers of articles were increased during 2017-2024. The majority of the birth cohort studies focused on the field of maternal health. Also, the most common research area among the five birth cohorts was environmental and occupational exposures.
The environmental factors, such as air pollution, allergens, pesticides, radiation, and chemical exposures during pregnancy, can significantly influence pregnancy outcomes and the long-term health of the child [6]. In Pandolfni’s study, consistent with our findings, environment research was a priority research area for cohorts in Europe [2]. Achievements of other birth cohort centers worldwide have provided information on immune disorders (such as allergic diseases and asthma), environmental exposure, neurocognitive development/neurobehavioral disorders, and nutrition [8-10]. In a review conducted by Vrijheid et al., growth and obesity, allergies, asthma, and respiratory infections were assessed in nearly all European birth cohorts [9].
Birth cohort studies across the globe have distinct original goals, yet they have also expanded into new research domains influenced by varying geographic contexts. In Brazil, for instance, violence represents a critical health and social issue, ranking as the leading cause of mortality among children and adolescents [4]. Hence, a new focus of the cohort is to understand the effects of violence on child development and health. A new area for research is the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and children’s health and the birth cohort achievements [7, 11]. According to the experiences of birth cohort centers in the world, face-to-face interviews were suspended during the COVID-19 pandemic [7, 12]. In Pearson’s study [12], COVID-19 changed the way the study team interacted with the cohort and impacted the cohort’s health outcomes. The PERSIAN birth cohort teams from five universities made efforts to carry out research related to COVID-19, aligning with the policies of the Corona National Anti-Virus Headquarters, and the Minister of Health and Medical Education [13, 14]. During the COVID-19 pandemic, facilities such as distributing preventive measures like alcohol, gloves, and masks, as well as conducting polymerase chain reaction tests, were provided.
The designs of the majority of published studies are observational; however, they serve as a suitable platform for clinical research. Involving pregnant women in research studies is crucial for gathering essential information about the safety and effectiveness of therapeutics or interventions aimed at improving maternal health and pregnancy outcomes [15]. Since pregnant women are typically excluded from randomized controlled trials for ethical reasons, it is difficult to evaluate the safety of drugs used during pregnancy. In this regard, designs of observational population-based cohort studies offer an alternative to randomized controlled trials [3]. This approach can yield valuable insights without the costs, risks, and ethical concerns associated with clinical trials.
Among the five centers, the Isfahan birth cohort center produced the most published scientific articles, followed by Semnan and Sari, respectively. The findings also revealed that the majority of scientific articles have originated from a single center. Multi-center studies can pool resources and expertise, enhancing the overall quality of research. The birth cohort studies can be a suitable platform for sharing data to achieve their common goals.
To enhance future birth cohort studies in Iran, several practical suggestions can be made based on the current structure and objectives of the PERSIAN Birth Cohort. We suggest that the PERSIAN birth cohort engage in collaborative efforts to enhance the study’s validity. Future studies should focus on incorporating a wider diversity of ethnicities and geographical regions. This will facilitate the identification of the distinct cultural, genetic, and environmental factors that impact health outcomes. Also, integrating socioeconomic status into the study design can offer valuable insights into health disparities. Evidence from studies highlights the significant influence of socioeconomic factors on health outcomes. By adopting these practical recommendations, future birth cohort studies can achieve more meaningful results that significantly enhance public health knowledge and lead to interventions specifically designed to meet the needs of the Iranian population.
Conclusion
The results of this review showed that the environmental and occupational exposures in the maternal field were the most common research area, deriving from five PERSIAN birth cohorts. The findings also indicated that most studies were conducted independently. Consequently, it is recommended that the five PERSIAN birth cohort centers collaborate in future research to identify the cultural, genetic, and environmental factors that influence health outcomes.
Study strengths and limitations
Based on the available knowledge, this study is the only document that focuses on the achievements related to the PERSIAN birth cohort centers. The main limitation of our research was the lack of access to the full text of some studies, which hindered our ability to identify the study design and research area. In response, we contacted the authors of those studies and requested that they provide us with the full text of their articles. Despite our efforts to address this issue, we have no access to the full text of some studies. Additionally, identifying the research area in some studies was difficult.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran (Code: IR.MAZUMS.REC.1401.464).
Funding
This study was funded by the Deputy of Research and Technology of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran (Code: 15032).
Authors contributions
Conceptualization, supervision: Mohammad Sadegh Rezai; Data curation, writing the original draft: Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, and Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi; Review, and editing: Mohammad Sadegh Rezai, Fereshteh Rostami-Maskopaee, Mehran Asadi-Aliabadi, and Mahmood Moosazadeh; Final approval: All authors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors are deeply thankful to the members of the PERSIAN birth cohort research team from five universities of medical sciences.
References
- Wang X, Kattan MW. Cohort studies: Design, analysis, and reporting. Chest. 2020; 158(1):S72-8 [DOI:10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.014] [PMID]
- Pandolfini C, Ricci C, Siziba LP, Huhn S, Genuneit J, Bonati M. Intrauterine Exposures and Maternal Health Status during Pregnancy in Relation to Later Child Health: A review of pregnancy cohort studies in Europe. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(14):7702. [DOI:10.3390/ijerph18147702] [PMID] [
- Canova C, Cantarutti A. Population-based birth cohort studies in epidemiology. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17(15):5276. [DOI:10.3390/ijerph17155276] [PMID]
- Rönkä AR, Sailo A, Hirvonen N. Six decades of longitudinal health knowledge production: A systematic review on Nordic birth cohort studies. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2023; 82(1):2278815. [DOI:10.1080/22423982.2023.2278815] [PMID]
- McDonald SW, Lyon AW, Benzies KM, McNeil DA, Lye SJ, Dolan SM, et al. The All Our Babies pregnancy cohort: Design, methods, and participant characteristics. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2013; 13(Suppl 1):S2. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2393-13-S1-S2] [PMID]
- Zare Sakhvidi MJ, Danaei N, Dadvand P, Mehrparvar AH, Heidari-Beni M, Nouripour S, et al. The prospective epidemiological research studies in IrAN (PERSIAN) birth cohort protocol: Rationale, design and methodology. Longit Life Course Stud. 2021; 12(2):241-62. [DOI:10.1332/175795920X16062247639874]
- Lin Y, Jiang Y, Du J, Ma H, Shen H, Hu Z. The continuing evolution of birth cohort studies: achievements and challenges†. Biol Reprod. 2022; 107(1):358-67. [DOI:10.1093/biolre/ioac117] [PMID]
- Pansieri C, Pandolfini C, Clavenna A, Choonara I, Bonati M. An inventory of European Birth Cohorts. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3071. [DOI:10.3390/ijerph17093071] [PMID]
- Vrijheid M, Casas M, Bergström A, Carmichael A, Cordier S, Eggesbø M, et al. European birth cohorts for environmental health research. Environ Health Perspect. 2012; 120(1):29-37. [DOI:10.1289/ehp.1103823] [PMID]
- Larsen PS, Kamper-Jørgensen M, Adamson A, Barros H, Bonde JP, Brescianini S, et al. Pregnancy and birth cohort resources in Europe: A large opportunity for aetiological child health research. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2013; 27(4):393-414. [DOI:10.1111/ppe.12060] [PMID]
- Murray J, Leão OAA, Flores TR, Demarco FF, Tovo-Rodrigues L, Oliveira IO, et al. Cohort Profile Update: 2015 Pelotas (Brazil) Birth Cohort Study-follow-ups from 2 to 6-7 years, with COVID-19 impact assessment. Int J Epidemiol. 2024; 53(3):dyae048. [DOI:10.1093/ije/dyae048] [PMID]
- Pearson C, Bartell T, Wang G, Hong X, Rusk SA, Fu L, et al. Boston Birth Cohort profile: Rationale and study design. Precis Nutr. 2022; 1(2):e00011. [PMID]
- Shahbaznejad L, Navaeifar MR, Movahedi FS, Hosseinzadeh F, Fahimzad SA, Serati Shirazi Z, et al. Knowledge, attitude and practice of Sari birth cohort members during early weeks of COVID-19 outbreak in Iran. BMC Public Health. 2021; 21(1):982. [DOI:10.1186/s12889-021-11039-6] [PMID]
- Mirmohammadkhani M, Bemanalizadeh M, Yazdi M, Goli P, Mohebpour F, Saffarieh E, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices toward covid-19 among persian birth cohort participants. J Educ Health Promot. 2021; 10:358. [DOI:10.4103/jehp.jehp_1274_20] [PMID]
- McKiever M, Frey H, Costantine MM. Challenges in conducting clinical research studies in pregnant women. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2020; 47(4):287-93. [DOI:10.1007/s10928-020-09687-z] [PMID]
- Eghtesad S, Mohammadi Z, Shayanrad A, Faramarzi E, Joukar F, Hamzeh B, et al. The PERSIAN Cohort: Providing the evidence needed for healthcare reform. Arch Iran Med. 2017; 20(11):691-5. [PMID]
- Poustchi H, Eghtesad S, Kamangar F, Etemadi A, Keshtkar AA, Hekmatdoost A, et al. Prospective epidemiological research studies in Iran (the PERSIAN Cohort Study): Rationale, objectives, and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2018; 187(4):647-55. [DOI:10.1093/aje/kwx314] [PMID]
- Darvishmotevalli M, Bina B, Feizi A, Ebrahimpour K, Pourzamani H, Kelishadi R. Monitoring of urinary phthalate metabolites among pregnant women in Isfahan, Iran: The PERSIAN birth cohort. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2019; 17(2):969-78. [DOI:10.1007/s40201-019-00412-8] [PMID]
- Fadaei S, Pourzamani H, Ebrahimpour K, Feizi A, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. Association of maternal urinary concentration of parabens and neonatal anthropometric indices. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2020; 18(2):617-28. [DOI:10.1007/s40201-020-00487-8] [PMID]
- Darvishmotevalli M, Moradnia M, Hosseini R, Bina B, Feizi A, Ebrahimpour K, et al. Association between prenatal phthalate exposure and anthropometric measures of newborns in a sample of Iranian population. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021; 28(36):50696-706. [DOI:10.1007/s11356-021-14182-0] [PMID]
- Fadaei S, Pourzamani H, Ebrahimpour K, Feizi A, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. Investigating determinants of parabens concentration in maternal urine. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J. 2021; 27(3):668-86. [DOI:10.1080/10807039.2020.1750344]
- Amin MM, Ghasemi Z, Khoshhali M, Taheri E, Dehdashti B, Fatehizadeh A, et al. Association of maternal exposure to bisphenol A with her β-hCG level and neonatal anthropometric measures. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021; 28(44):62809-15. [DOI:10.1007/s11356-021-15094-9] [PMID]
- Moradnia M, Movahedian Attar H, Heidari Z, Mohammadi F, Kelishadi R. Monitoring of urinary arsenic (As) and lead (Pb) among a sample of pregnant Iranian women. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021; 19(2):1901-9. [DOI:10.1007/s40201-021-00743-5] [PMID]
- Moradnia M, Attar HM, Heidari Z, Mohammadi F, Kelishadi R. Prenatal exposure to chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) in a sample of Iranian pregnant women: Urinary levels and associated socio-demographic and lifestyle factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021; 28(44):63412-21. [DOI:10.1007/s11356-021-15201-w] [PMID]
- Navaifar MR, Rahimzadeh G, Fahimzad AR, Safar MJ, Shamshiri AR, Rezai S, et al. [Seroepidemiology of hepatitis B in pregnant women in Sari, Iran 2018-2020 (Persian)]. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2021; 30(194):121-6. [Link]
- Rahimzadeh G, Shahbaznejad L, Fahimzad A, Safar MJ, Movahedi FS, Rezai S, et al. [Seroepidemiology of Cytomegalovirus in Pregnant Women in Sari, Iran 2018-2020 (Persian)]. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2021; 31(202):149-54. [Link]
- Golestanzadeh M, Ebrahimpour K, Daniali SS, Zarean E, Yazdi M, Basirat Z, et al. Association between parabens concentrations in human amniotic fluid and the offspring birth size: A Sub-study of the PERSIAN birth cohort. Environ Res. 2022; 212(Pt D):113502. [DOI:10.1016/j.envres.2022.113502] [PMID]
- Dehdashti B, Feizi A, Arvin A, Bagheri N, Daniali SS, Amin MM, et al. Urinary brominated trihalomethanes among pregnant women: Correlation with lifestyle factors. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J. 2022; 28(8):878-92. [Link]
- Taheri E, Amin MM, Daniali SS, Abdollahpour I, Fatehizadeh A, Kelishadi R. Health risk assessment of exposure to chlorpyrifos in pregnant women using deterministic and probabilistic approaches. Plos One. 2022; 17(1):e0262127.[DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0262127] [PMID]
- Yazdi M, Bemanalizadeh M, Mohebpour F, Goli P, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. Latent class analysis of knowledge, attitude, and practice of a population-based sample of Iranian pregnant women toward COVID-19. Adv Biomed Res. 2022; 11:52. [DOI:10.4103/abr.abr_271_21] [PMID]
- Attarian E, Ebrahimpour K, Maracy M, Daniali SS, Shoshtari-Yeganeh B, Moazeni M, et al. Effect of maternal triclosan exposure on neonatal thyroid-stimulating hormone levels: A cross-sectional study. J Environ Public Health. 2022; 2022:3082304. [DOI:10.1155/2022/3082304] [PMID]
- Golestanzadeh M, Goodarzi-Khoigani M, Shahrbanoo Daniali S, Ebrahimpour K, Zarean E, Yazdi M, et al. Association between phthalate metabolites in human amniotic fluid and offspring birth size: A sub-study of the PERSIAN birth cohort. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022; 29(51):76970-82. [DOI:10.1007/s11356-022-20839-1] [PMID]
- Teiri H, Samaei MR, Dehghani M, Azhdarpoor A, Hajizadeh Y, Mohammadi F, et al. The association of prenatal exposure to benzophenones with gestational age and offspring size at birth. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022; 29(17):24682-95. [DOI:10.1007/s11356-021-17634-9] [PMID]
- Rahimzadeh G, Safar MJ, Rezai S, Rezai MS, Movahedi FS. Seroepidemiology of HBV, HCV, HIV, HTLV, and CMV in Pregnant Women Referring to Sari Birth Cohort. Adv Biomed Res. 2022; 11:97. [DOI:10.4103/abr.abr_334_22] [PMID]
- Daniali SS, Yazdi M, Heidari-Beni M, Taheri E, Zarean E, Goli P, et al. Birth size outcomes in relation to maternal blood levels of some essential and toxic elements. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023; 201(1):4-13. [DOI:10.1007/s12011-022-03121-w] [PMID]
- Bahreynian M, Feizi A, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. Interaction between maternal dietary fat intake, breast milk omega-3 fatty acids and infant growth during the first year of life. Child Care Health Dev. 2023; 49(1):137-44. [DOI:10.1111/cch.13026] [PMID]
- Askari M, Dadbinpour A, Ekraminasab S, Shukohifar M. Incidence and risk factors related to gestational diabetes mellitus among women in Yazd: A prospective cohort study. World J Peri Neonatol. 2023; 5(2):65-73. [Link]
- Amini N, Mousavi S, Vard B, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. The assessment of neonatal anthropometric indices association with umbilical cord blood zinc and magnesium levels. Adv Biomed Res. 2023; 12:253. [DOI:10.4103/abr.abr_90_23] [PMID]
- Mohtashaminia F, Hosseini F, Jayedi A, Mirmohammadkhani M, Emadi A, Takfallah L, et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and risk of gestational diabetes: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023; 23(1):647. [DOI:10.1186/s12884-023-05960-4] [PMID]
- Jayedi A, Zeraattalab-Motlagh S, Moosavi H, Mirmohammadkhani M, Emadi A, Shab-Bidar S. Association of plant-based dietary patterns in first trimester of pregnancy with gestational weight gain: Results from a prospective birth cohort. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2023; 77(6):660-7. [DOI:10.1038/s41430-023-01275-x] [PMID]
- Teiri H, Samaei MR, Dehghani M, Azhdarpoor A, Mohammadi F, Kelishadi R, et al. Maternal exposure to benzophenone derivatives and their impacts on offspring's birth outcomes in a Middle Eastern population. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):9484. [DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-35380-5] [PMID]
- Pormazar SM, Banadaki MD, Jambarsang S, Ehrampoush MH, Mehrparvour AH, Nakhostin F, et al. The impact of ambient air pollutants on birth outcomes using ARMA Model: Yazd mother and birth cohort study. J Environ Health Sustain Dev. 2023 [DOI:10.18502/jehsd.v8i3.13703]
- Daniali SS, Abdoli M, Heidari-Beni M, Khoshhali M, Kelishadi R. Trend of physical activity and sedentary time during pregnancy and related determinants. J Public Health. 2023; 33:831-41. [DOI:10.1007/s10389-023-02059-0]
- Dehghan-Banadaki S, Hosseinzadeh M, Madadizadeh F, Mozaffari-Khosravi H. Empirically derived dietary patterns and postpartum depression symptoms in a large sample of Iranian women. BMC Psychiatry. 2023; 23(1):422 [DOI:10.1186/s12888-023-04910-w] [PMID]
- Golverdi E, Hashemipour M, Hovsepian S, Khoshhali M, Kelishadi R. Associations between Prenatal Exposure to Air Pollutants and Cord-Blood Thyroid Hormones Levels: A cross-sectional study in Isfahan. Int J Pediatr. 2024; 12(3):18637-48. [DOI:10.22038/ijp.2024.79827.5454]
- Alimardani B, Hashemipour M, Hovsepian S, Mozafarian N, Khoshhali M, Kelishadi R. Association between maternal and cord blood thyroid hormones, and urine iodine concentration with fetal growth. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024; 37(6):516-24. [DOI:10.1515/jpem-2023-0570] [PMID]
- Taheri E, Goodarzi-Khoigani M, Riahi R, Daniali SS, Kelishadi R. Urinary Cadmium in Relation to Neonatal Anthropometric Indices during Pregnancy. Int J Environ Health Eng. 2024; 13(1):12. [DOI:10.4103/ijehe.ijehe_65_22]
- Yazdi M, Bemanalizadeh M, Kelishadi R. Persian version of brief infant sleep questionnaire (BISQ): A psychometric evaluation. BMC Pediatr. 2024; 24(1):181. [DOI:10.1186/s12887-024-04666-6] [PMID]
- Jamali M, Heidari-Beni M, Khoshhali M, Naderiboldaji S, Ghiasvand R, Kelishadi R. [Associations between dietary patterns during pregnancy and neurodevelopment in children (Persian)]. Iran J Nutr Sci Food Technol. 2024; 19(1):39-58. [Link]
- Pourmirzaiee MA, Daniali SS, Riahi R, Majidi S, Kelishadi R. Association of postpartum depression with maternal serum magnesium levels, infant growth, and neurodevelopmental indices. Int J Prev Med. 2024; 15:16. [DOI:10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_30_24] [PMID]
- Hashemi Dehkordi V, Khoshhali M, Heidari-Beni M, Hashemi Dehkordi E, Hashemipour M, Mostofizadeh N, et al. Association Between Dietary Phytochemical Index and neonatal thyroid function. J Pregnancy. 2024; 2024:9558023 [DOI:10.1155/2024/9558023] [PMID]
- Ganjeh BJ, Mirrafiei A, Jayedi A, Mirmohammadkhani M, Emadi A, Ehsani F, et al. The relationship between adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern during early pregnancy and behavioral, mood and cognitive development in children under 1 year of age: A prospective cohort study. Nutr Neurosci. 2024; 27(7):726-33. [DOI:10.1080/1028415X.2023.2249635] [PMID]
- Norouziasl R, Jayedi A, Mirmohammadkhani M, Emadi A, Aghaamo S, Shab-Bidar S. Consumption of red and processed meat during early pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes: A prospective birth cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):5209. [DOI:10.1038/s41598-024-55739-6] [PMID]
- Baradaran Mahdavi S, Javadirad SM, Rafieian M, Poursafa P, Azimian Zavareh V, Daniali SS, et al. A procedure for DNA methylation assessment in osteoporosis-related gene promoters of umbilical cord blood: A study on the Prospective Epidemiological Research Studies in Iran (PERSIAN) birth cohort. Bioimpacts. 2024; 15:30095. [PMID]
Type of Study: Systematic Review |
Subject:
Pediatrics
Received: 2024/11/25 | Accepted: 2025/01/23 | Published: 2025/04/1
Received: 2024/11/25 | Accepted: 2025/01/23 | Published: 2025/04/1
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |






